Cloud Computing: The Future of IT Infrastructure
In today’s digital age, technology is advancing at an unprecedented pace. One such technology that has gained immense popularity in recent years is cloud computing. Cloud computing is a revolutionary concept that has transformed the way we store, access, and manage data. we will delve into the world of cloud computing, exploring its definition, benefits, and applications.
What is Cloud Computing?
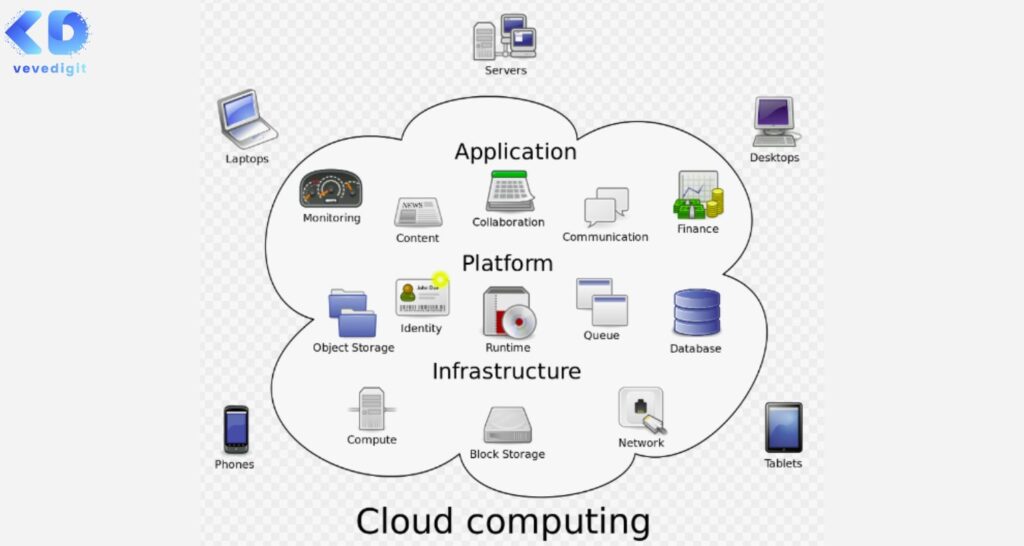
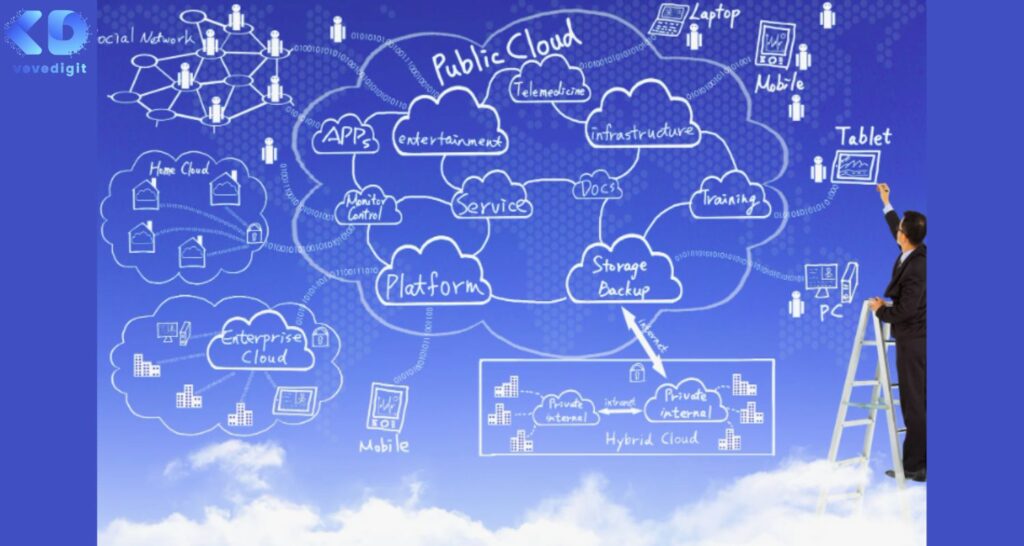
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of on-demand computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the internet to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. In simpler terms, cloud computing allows users to access and use computing resources and services through the internet instead of relying on local servers or personal devices.
The term “cloud” is used as a metaphor for the internet because it is not visible to the naked eye. The cloud is a network of remote servers hosted by third-party service providers that offer various services such as storage, processing power, and software applications. These servers are connected through high-speed networks and can be accessed from anywhere in the world with an internet connection.
Cloud Computing Benefits
Scalability: One of the most significant benefits of cloud computing is scalability. Cloud service providers offer flexible resource allocation options that allow users to scale up or down their resources based on their needs. This means that users can easily add or remove resources as their requirements change without having to invest in expensive hardware or infrastructure.
Cost-effective: Cloud computing eliminates the need for organizations to invest in expensive hardware and infrastructure for their IT needs. Instead, they can pay for only the resources they use on a pay-as-you-go basis. This results in significant cost savings as organizations no longer have to bear the capital expenditure associated with traditional IT infrastructure.
Accessibility: Cloud computing enables users to access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This means that users can work from home, office, or any other location without having to carry their laptops or other devices with them. This also ensures business continuity in case of natural disasters or other unforeseen events that may disrupt traditional IT infrastructure.
Security: Cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures to ensure that their customers’ data is protected from unauthorized access or theft. They use advanced encryption techniques and multi-factor authentication to secure user data and prevent data breaches. Additionally, cloud service providers offer backup and disaster recovery solutions that ensure business continuity in case of any unforeseen events.
Collaboration: Cloud computing facilitates collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and edit the same document simultaneously from different locations. This eliminates the need for emailing documents back and forth and ensures that everyone has access to the latest version of the document. This also facilitates real-time communication and collaboration among team members working on a project from different locations.
Applications of Cloud Computing
Storage: Cloud storage services allow users to store their data on remote servers instead of local devices such as hard drives or USB sticks. This eliminates the need for expensive hardware investments and ensures data security and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. Examples of popular cloud storage services include Google Drive, Dropbox, and Microsoft OneDrive.
Computing: Cloud computing allows users to access powerful computing resources such as servers, processors, and storage over the internet instead of relying on local devices or servers. This enables organizations to run complex applications such as machine learning algorithms or large-scale simulations without having to invest in expensive hardware infrastructure. Examples of popular cloud computing services include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Software: Cloud service providers offer a wide range of software applications such as productivity tools, collaboration platforms, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems over the internet instead of requiring users to install them locally on their devices or servers. This eliminates the need for expensive software licenses and ensures that users always have access to the latest version of the software without having to worry about updates or maintenance issues. Examples of popular cloud software applications include Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce CRM, and SAP SuccessFactors ERP system.
The Future of Cloud Computing

As cloud computing continues to gain popularity, it is clear that this technology will continue to evolve and transform the way we do business in the future. Here are some trends and predictions for the future of cloud computing:
Multi-cloud: As more organizations adopt cloud computing solutions, it is likely that they will use multiple cloud service providers to meet their specific needs. This is known as multi-cloud, which allows organizations to leverage the strengths of multiple cloud service providers instead of relying on a single provider. Multi-cloud also provides organizations with greater flexibility, resilience, and cost savings by allowing them to choose the best cloud service provider for each application or workload.
Edge Computing: Edge computing refers to the processing of data at the edge of a network, close to the source of the data, instead of sending it to a centralized cloud server for processing. This reduces latency and improves response times, making it ideal for applications such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. Edge computing also reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, resulting in cost savings and improved efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Cloud service providers are investing heavily in AI and ML technologies to provide their customers with advanced analytics, insights, and predictions based on their data. AI and ML algorithms can analyze large volumes of data in real-time, enabling organizations to make informed decisions quickly and accurately. Cloud service providers are also offering pre-trained ML models that can be easily integrated into applications, making it easier for organizations to leverage AI and ML technologies without having to invest in expensive hardware or infrastructure.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing refers to a model where cloud service providers manage the infrastructure required to run an application, eliminating the need for organizations to manage their own servers or infrastructure. This results in significant cost savings as organizations no longer have to bear the capital expenditure associated with traditional IT infrastructure. Serverless computing also provides organizations with greater scalability and flexibility as they only pay for the resources they use on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Cybersecurity: As more organizations adopt cloud computing solutions, cybersecurity will become a critical concern for cloud service providers and their customers alike. Cloud service providers are investing heavily in cybersecurity measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access control mechanisms to ensure that their customers’ data is protected from unauthorized access or theft. Organizations will also need to ensure that they have robust cybersecurity policies and procedures in place to protect their data both in the cloud and on-premises.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we store, access, and manage data by offering scalability, cost-effectiveness, accessibility, security, and collaboration capabilities that traditional IT infrastructure cannot match. As more organizations adopt cloud computing solutions for their IT needs, it is clear that this technology will continue to transform the way we do business in the future by enabling faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale for organizations of all sizes across various industries worldwide.
FAQs
Cloud computing offers several benefits, including scalability, cost savings, flexibility, accessibility, and improved collaboration.
Cloud providers use advanced security measures to protect data, including encryption, access controls, and regular backups. However, it’s still important for users to follow best practices for data security, such as using strong passwords and limiting access to sensitive information.
Most types of applications can be run in the cloud, including web applications, databases, analytics tools, and virtual desktops.
To get started with cloud computing, you’ll need to sign up for a cloud service provider (CSP) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers offer a range of services and tools to help you get started.
Multi-cloud computing involves using multiple CSPs to meet your organization’s specific needs. This can provide greater flexibility and redundancy than relying on a single CSP.




