Introduction to Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology is not just a buzzword; it’s a paradigm shift in how we perceive and manage physical entities. At its core, a digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system, be it a machine, a building, or even an entire city. This representation is not static but dynamic, mirroring real-world changes in real-time.
Evolution and Origins
The roots of digital twin technology can be traced back to the concept of cyber-physical systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). As our ability to collect and process data advanced, so did the possibilities of creating detailed digital replicas.
How Digital Twin Technology Works

Understanding the functionality of Digital twin technology involves grasping the intricacies of data collection, integration, and real-time monitoring.
Data Collection and Integration
Digital twins thrive on data. Sensors embedded in physical entities gather data points, feeding them into the digital replica. This integration of real-world data allows for a high-fidelity representation that evolves as the physical entity changes.
Real-time Monitoring and Analysis
The true power of digital twin technology lies in its ability to monitor and analyze the real-time data received from the physical counterpart. This enables stakeholders to make informed decisions promptly, enhancing overall efficiency.
Key Components of Digital Twin Technology
For a digital twin to function seamlessly, several key components come into play.
Sensor Networks
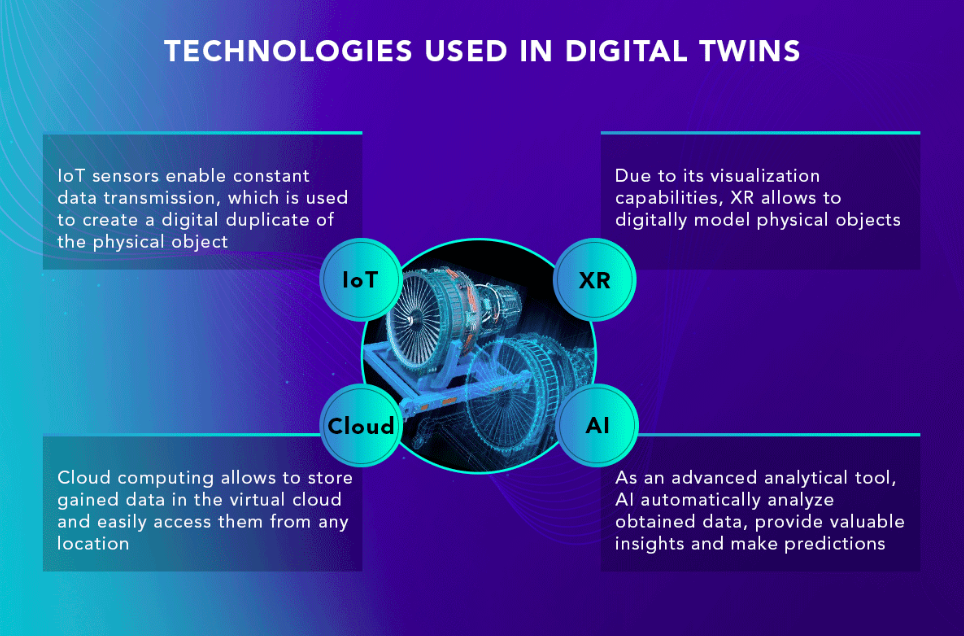
Sensors act as the eyes and ears of digital twins. They capture data on various parameters, ensuring the virtual replica stays synchronized with its physical counterpart.
Cloud Computing
The vast amount of data generated by digital twins necessitates robust computing capabilities. Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure for storage, processing, and analysis.
Advanced Analytics
The data collected needs to be translated into meaningful insights. Advanced analytics, including machine learning algorithms, play a crucial role in extracting actionable information from the vast datasets.
Applications Across Industries
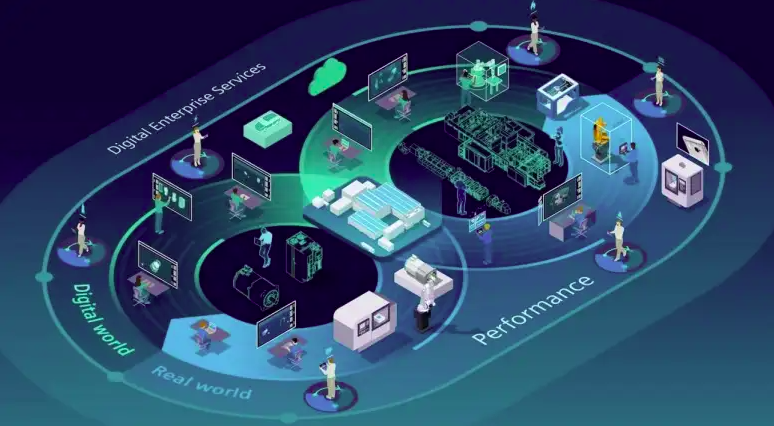
Digital twin technology has found applications across diverse industries, each reaping unique benefits.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, digital twins optimize processes, streamline production, and facilitate predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
Healthcare
In healthcare, digital twins contribute to personalized medicine, allowing for virtual simulations of individual patients for more accurate diagnostics and treatment plans.
Smart Cities
The concept of smart cities is greatly empowered by digital twin technology. It enables efficient urban planning, resource management, and the creation of sustainable living environments.
Benefits of Digital Twin Technology
The adoption of digital twin technology comes with a myriad of advantages.
Improved Efficiency
By providing real-time insights and facilitating predictive analysis, digital twins enhance operational efficiency, minimizing errors and downtime.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance, made possible by digital twin technology, ensures that issues are identified and addressed before they escalate, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of assets.
Enhanced Decision-Making
The wealth of data generated and analyzed by digital twins empowers decision-makers with accurate, timely information, leading to more informed choices.
Challenges and Limitations
However, the road to widespread adoption is not without its challenges.
Digital Twin Technology in the Future
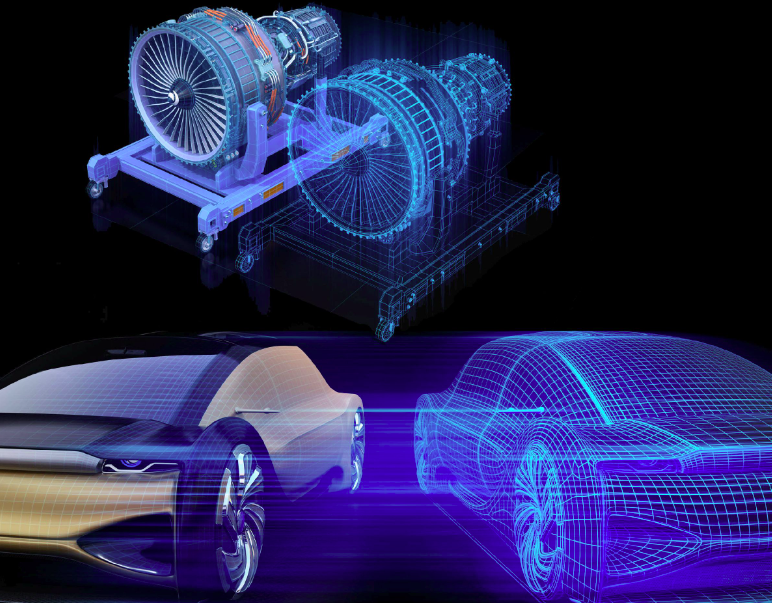
Looking ahead, Digital twin technology is poised for even greater advancements.
Emerging Trends
Trends such as edge computing, 5G technology, and the continued evolution of AI are set to further enhance the capabilities of digital twins.
Potential Innovations
Innovations like real-time simulation and the integration of augmented reality hold the promise of taking digital twin technology to unprecedented levels of sophistication.
Comparisons with Traditional Technologies
To appreciate the full scope of digital twin technology, let’s compare it to traditional systems.
Advantages Over Conventional Systems
The advantages, including real-time insights and predictive capabilities, position digital twins as superior to traditional technologies.
Regulatory Landscape
As digital twin technology matures, regulatory frameworks are evolving.
Current Regulations
An overview of existing regulations governing the use of digital twin technology.
Future Expectations
Anticipated developments in regulatory frameworks to address emerging challenges.
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Gains
While the initial investment may seem substantial, the long-term gains in efficiency and cost savings often outweigh the costs.
Digital Twin Technology and IoT Synergy
Examining the interconnected nature of digital twin technology with the broader IoT ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Digital twin technology stands as a testament to human ingenuity. Its impact spans industries, reshaping how we approach challenges and optimize processes. As we stand on the cusp of even greater technological advancements, the future of digital twin technology looks promising, offering solutions to complex problems and unlocking new possibilities.
FAQs
No, digital twin technology can be scaled to fit the needs of various industries, regardless of size.
Robust encryption and access controls are implemented to secure sensitive data associated with digital twins.
Yes, ethical considerations, such as patient consent and data transparency, are crucial in healthcare applications.
Yes, while it may pose challenges, retrofitting digital twin technology is feasible with proper planning.
Artificial intelligence is integral to digital twin technology, powering advanced analytics and decision-making processes.





